|
|
![]()
FOREST HEALTH - SOFTWOOD STEM & TRUNK DISEASES
The rich vascular tissue in the live portion of trunks and branches lies under the bark. Cellulose-rich wood lies inside the vascular tissue. These tissues are the target of a large number of pathogens and wood-rotting fungi. Symptoms are commonly the wilting of leaves or fruiting bodies (e.g. conks) outside the bark. Some are relatively harmless to the trees, while others are fatal. Many diseases degrade wood quality and result in the loss of billions of dollars of monetary value each year. Disease is, by far, the top cause of tree mortality. Biologically, many of these diseases are interesting and are an essential component of a healthy forest ecosystem. Wood rotting fungi provide habitat for a large number of insects, birds, mammals, and other wildlife. Some are even edible. On the other hand, certain exotic species have wreaked havoc on our eastern forests, and there are more to come. Red text indicates an exotic pest.
| Cankers
Dwarf Mistletoe Trunk Rots White Pine Blister Rust |
|
| Cankers (several species): cankers will often infect a tree through wounds, often from buds, needles, or twigs; the fungi can progress to branches and stems and potentially kill the tree; early symptoms are browning needles in isolated spots; Sclerroderris (Gremmeniella abietina) attacks mostly red & jack pines though the buds and then into the stems, green inner bark of twigs, European strain more virulent; Cytospora (Cytospora kunzei) affects spruces but stem cankers are hard to find, usually affects lower branches first | |
| Hosts: all conifers | |
 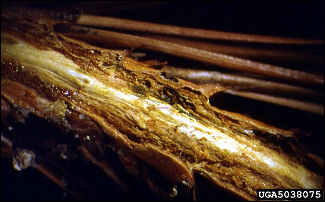  [Gremmeniella (2), Cytospora] |
|
|
|
| Hosts: mostly spruces & tamarack | |
  [dwarf mistletoe] |
|
Stem Rusts (Cronartium spp.): eastern gall rust (Cronartium quercuum) can kill younger trees and cause breaking points on older trees, oak alternate host; sweet fern rust (C.comptoniae), stalactiform rust (C.coleosporioides), and Comandra rust (C.comandrae) can kill or can render trees more vulnerable to other damaging agents |
|
| Hosts: jack and Scots pines | |
    [C.querccum, C.comptoniae, C.coleosporioides, C.comandrae] |
|
Trunk Rots (several genera): these fungi enter a tree through wounds and consume the cellulose of the sapwood and/or heart wood, structural weakness can lead to breakage, most form form conks (fruiting bodies), some root rots can extend into the trunks (see root rots) |
|
| Hosts: fir-Norway spruce-white pine (red heart of fir-Stereum sanguinolentum), most conifers (red heart of pine-Onnia pini) | |
  [Stereum sanguinolentum, Onnia pinii] |
|
White Pine Blister Rust (Cronartium ribicola): kills stem and branch tissue, look for orange bark and then sunken or split tissues, white sap drips common (from other injury, too), dead tops on trees, alternate host Ribes spp. (gooseberries & currants), eliminates white pine in some areas, introduced about 1906 |
|
| Hosts: eastern white pine | |
|
|
Image Citations
Scleroderris Canker (1) - USDA Forest Service - North Central Research Station Archive, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Scleroderris Canker (2) - USDA Forest Service - Northeastern Area Archive, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Cytospora Canker - Joseph O'Brien, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Mistletoe (2) - Joseph O'Brien, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Eastern Gall Rust - Robert L. Anderson, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Sweet Fern Rust - USDA Forest Service - North Central Research Station Archive, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Stalactiform Rust - USDA Forest Service Archive, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Comandra Rust -
Brian Geils, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Red Heart of Fir - Andrej Kunca, National Forest Centre - Slovakia, Bugwood.org
Red Heart of Pine - Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Archive, Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, Bugwood.org
Annosum Root Rot (1) - USDA Forest Service - Region 8 - Southern Archive, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Annosum Root Rot (2) - USDA Forest Service Archive, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
Annosum Root Rot (3) - USDA Forest Service - Pineville Archive, USDA Forest Service, Bugwood.org
All others - Bill Cook, Michigan State University Extension
Click HERE
to return to the U.P. Tree ID home page.
Click HERE to return to the Forest Health home page.
This site created and maintained by Bill Cook, MSU Extension Forester for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. Editing and modification is ongoing. Submit suggestions, questions, and corrections to cookwi@msu.edu or call 906-786-1575.